The importance of keyword research in search engine optimisation is a topic that has been discussed for many years. It’s now more important than ever as search engines are becoming smarter and have the ability to filter out content they don’t see fit for their users. This means that if you want your content to be found by people who are looking for it, you’ll need to make sure that you’re using keywords in your writing and on your site that will help it rank higher.
You’ve probably heard some of this information before, but now you can see what the future holds! In this article, we will discuss:
1. Understanding how webpages are ranked
2. Keyword research tips
3. How to use keywords in an article
4. What is user intent and entity search, and how does it affect your content strategy
5. Why understanding the importance of keyword research will help you rank higher on Google’s SERPs in 2021
To do keyword research, you need to be willing to experiment and think outside of the box. The importance of keyword research is clear in today’s world, where search engines are increasingly more intelligent, and users are more adept at searching online. Search engines know what their users want and filter out content that is not relevant for them, while users are asking more questions online than ever before. This means that keywords can create a huge impact on how your content ranks and is found online. It’s also important to write about semantically relevant topics in clusters so that each paragraph contains its own group of keywords, which, when combined, support the main keyword of your article.
In 2021 and beyond, keyword research will be even more important than ever before, with sites like Google releasing more advanced algorithms every day!
Understanding how webpages are ranked
Googles BERT algorithm uses a natural language processing model to understand search queries better and understand the context of words in a query – you can now search for more conversational things.
Google’s search algorithm goes beyond understanding synonyms and the basic meaning of a query; it also tries to categorise the type of information you are looking for. It looks to see if the query is specific in nature or more broad and if the query has any local attributes and the type of language used. The freshness of the information being searched for is also considered, especially for topics that have new information released regularly, like news or sports information.
Next, the search algorithm will analyse the content on webpages to try and find the most relevant content for a query. It scans through the text looking for mentions of the search query, taking into account the use of certain markup on a webpage (titles, H tags, alt text etc..).
The algorithm then has to rank all the pages found to potentially hold relevant information and work out which pages match the search query best. Analysing hundreds of different factors, the algorithm will deliver the top 10 results on the first page of Google and rank the rest of the webpages it found accordingly.
It also analyses the usability of webpages, looking for certain disruptions to users experience while they browse a page. These signals are sent back to the algorithm, which can then use this information as part of the ranking process.
Keyword research tips
The best way to find keywords that your audience is using is to do a little research on Google. You can type in specific questions or keywords and see what comes up. If you have a lot of traffic on your page already, likely, visitors are already using these keywords to find the information they need – you can get this information from Google Search Console. But if you don’t have a huge amount of traffic (or any at all), then you’ll want to use other methods.
As with most things in life, there are many different ways to do keyword research. The most popular way is through Google Keyword Planner, free keyword tools like KeywordTool.io or Ubersuggest and premium tools like SEMrush, LongTail Pro and SpyFu.
Here are some unique ways to carry out topically relevant keyword research:
Google search
Run a search in Google and scroll down to the bottom of the page. Here, you will find Related Searches – suggestions from Google on search queries that are highly related to what you just typed in, often what other people are also searching for.
Keywords Everywhere Chrome Extension
The Keyword Everywhere Chrome Extension is a must-have for any content marketer who needs to find the right keywords for their content. This extension makes it easy to generate keywords from your competitors’ sites and domains they might be targeting and trending topics around the web. You can also get suggestions based on the keyword you are typing into Google.
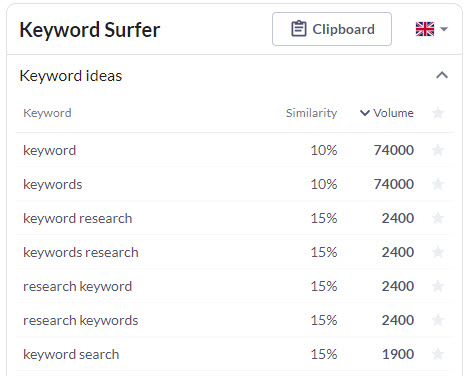
Keyword Surfer Chrome Extension
This is another great tool to help you uncover related keywords as you research in Google. Once you search for a keyword, a panel will appear on the right of the search results, showing you a list of related search terms with volume – Keyword Surfer will also shows the trend of the keyword.
Answer The Public
If you ever find yourself stuck while looking for keyword ideas, then Answer The Public is going to be your best friend. This tool uses a few different tactics to discover highly relevant keywords for any given topic. Just type in your main keyword or topic, and it will return a wide range of different keyword types, from questions that people are actually asking online to alphabetical suggestions.
How to use keywords in an article
Keywords can be added to your article in many places, but do not overdo it. You should focus on keywords that best describe the type of content you create and use semantically relevant terms to support your main keyword.
The best way to use keywords is through your headings (H1, H2, etc.) as these are used as signifiers for what your content is actually about.
Heading tags (H1-H6) and alt tags on images explain the context of your content by providing an extra signal for search engines, which is why keywords must be used in context when using these tags.
Heading tags add more information on what topics are being discussed throughout the page to find the information they are looking for quickly. The paragraph of text that follows should contain all the information suggested from the title of that paragraph; if a new subject is discussed, then a new title in an H tag should be used.
Headings also show search engines when an article is about a particular keyword or phrase. Keep in mind that Google and other search engines rank articles based on how many relevant keywords are used within them. So oftentimes, you’ll want to use the most specific keywords throughout your article – this will help get you noticed by the search engines much more effectively than using broad, non-descriptive terms.
How do I incorporate keywords into my content?
Try looking for opportunities within your writing: These can be places where the topic could naturally and easily flow from one point to another. There are “gaps” in the article where a keyword could fit or natural breaks within your content.
For every paragraph where you have a keyword in the H2 or H3, find the related keywords for this section using one of the methods above and try to use a few of these terms when it makes sense to do so.
Grouping your keywords at paragraph level before had will save a lot of time and allow you to plan your content brief efficiently.
What is user intent?

User intent is the purpose behind a user’s search query and is an extremely important part of the keyword research and content creation process.
Knowing your audience and its needs and knowing how to research them will help you find the right keywords that your customers are typing into search engines when seeking out products or services just like yours.
By understanding the intent behind keywords, you can create content that aligns with the needs of your audience and drive strong engagement.
What is entity search?
With thousands of search queries being run by people every day, there are many that Google doesn’t understand. Entity Search is the name given to those searches where Google returns results for a topic rather than returning results that match the actual search query itself. For example, if someone searches for “Champion by Jojo Moyes”, Google returns results on the book and not just links to sites that have the words “Champion” or “Jojo Moyes”.
Google knows that people are generally trying to find out more about a topic when searching for something like this instead of information about a specific site or page result. Trying to figure out exactly what people are searching for is tricky. Still, it has been an area of focus at Google for many years now, with their continuous efforts in refining it further so that users get the best possible results every time.
Although this is a hugely important part of optimisation for those who use entity search to help their SEO, it does not mean that Google has discounted the importance of exact match keywords. Many top-ranking sites still use exact match keywords within their content as part of well-structured SEO campaigns. There are many reasons why this could be, but ultimately, it is because it works. And for businesses that rely heavily on targeted traffic from Google, focusing efforts in this way will continue to make sense for a long time to come.
What are entities?
When people search for things, they generally use the name of a company, person or product. Google previously understood this to some extent, but it has now evolved to something known as “entities”, which is essentially just a broader term encompassing anything such as a brand name or trademark. This also includes proper nouns and other words that have been made into brands over time – such as ‘Facebook’ or ‘Honda’.
Google describes an entity as “A thing or concept that is singular, unique, well-defined and distinguishable.”
Entities are tricky for computers to understand because even if two people search for the same thing using slightly different terms, they could still be asking completely different questions. It’s like playing the game 20 Questions, where you have to guess what someone is thinking of by narrowing down possible answers based on their responses rather than directly asking them.
Google uses Wikipedia to identify entities in many scenarios, like providing information for Knowledge Panel. So anything that has a Wiki page is technically an entity, but entities can exist without a Wiki page!
Keywords should sit at the heart of all content strategies.
Without getting too technical, Google’s algorithm has changed over time to incorporate what they know about user intent when searching on the platform. This means that users looking for products or services tend to be given results based more on those topics rather than links that contain one of the words from their search query. It makes sense that you would need to structure your site more logically to try and maximise the chances of being featured within these results, especially when you consider that many people are now using Google as their main source of search.
If you have any online business, it is an excellent time to sit down and think about what your brand means. What makes your business different from others? Think about how you can tie this back into the keywords you will be targeting with content and link building initiatives over the next few months. You must identify what makes your website unique instead of just focusing solely on those exact match terms. Remember that millions of other businesses aim for almost the same keywords, so if your site has no true identity, it will be difficult to differentiate yourself in the long run. If you can figure out how your brand can stand out, you are well on your way to ensuring that Google keeps featuring your website for relevant searches over time.
Can keyword research get any better?
Although there is still a place for many of the techniques used in previous years, things have definitely changed since Google began integrating entity search into their algorithm. Now social media and recent news events must be factored into content creation alongside keywords and a natural structure if you want to ensure that people continue to find value in your site – which means being able to write for humans first! This is why creating interesting, engaging content with quality backlinks continues to be one of the most effective ways of achieving search engine success.
Why understanding the importance of keyword research will help you rank higher on Google’s SERPs in 2021
It is an undeniable fact that keyword research has changed a lot over time. In the past, you might have been able to get away with just doing some basic keyword research and then publishing some content based on the highest-ranking pages for your target search query. However, if you want to be successful in the future and rank higher within Google’s results pages, you will need more than this. The days when it was enough to write content targeted at search engines rather than people are long gone. Google continues their efforts towards improving user experience across the platform while cracking down harder on SEOs trying to manipulate their algorithm – but that doesn’t mean ignoring how the algorithm works.
Understanding the existing changes to Google’s algorithm because of entity search can put you at an advantage within the SERPs. It all comes down to focusing your efforts on creating valuable content for users rather than just for Google. Of course, it is still important that you try to target their results as effectively as possible with relevant keywords, but including relevant entities must now happen alongside keyword research.
Identifying entities within your content and optimising for these alongside keywords is where the magic lies. Google will be looking at entities within your content to understand better what the article is mainly focusing on, so a good way to help Google with this process is to add relevant entities to support main entities, the same way you would use LSI or secondary keywords to help support your main keyword.